:תתקשרו אלינו בטלפון
+972 (0)2 5665191
Edit Content
ד"ר ארי קופיאצקי
דיפלומט, המועצה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים
ברוכים הבאים למרפאתנו!ל
ניסיונו הנרחב של ד”ר קופיאצקי כולל עריכת מחקרי פלואוריד במעבדות המחקר של קולגייט-פאלמוליב וקבלת מלגת המחקר היוקרתית של קרן אלפא אומגה פעמיים במהלך לימודיו בחו”ל. מחקריו מתמקדים בטיפול שיניים בילדים צעירים מאוד, מה שמבטיח שהוא נשאר בחזית הטיפול ברפואת שיניים לילדים. ד”ר קופיאצקי הוא חבר מוערך בקהילה הדנטלית, שירת במועצת הייעוץ של המועצה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים וכחבר ודיפלומט באקדמיה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים.ל

ד"ר ארי קופיאצקי
דיפלומט, המועצה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים
ניסיונו הנרחב של ד"ר קופיאצקי כולל עריכת מחקרי פלואוריד במעבדות המחקר של קולגייט-פאלמוליב וקבלת מלגת המחקר היוקרתית של קרן אלפא אומגה פעמיים במהלך לימודיו בחו"ל. מחקריו מתמקדים בטיפול שיניים בילדים צעירים מאוד, מה שמבטיח שהוא נשאר בחזית הטיפול ברפואת שיניים לילדים. ד"ר קופיאצקי הוא חבר מוערך בקהילה הדנטלית, שירת במועצת הייעוץ של המועצה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים וכחבר ודיפלומט באקדמיה האמריקאית לרפואת שיניים לילדים.ל
30 שנות ניסיון!
במרפאתו במרכז ירושלים, ד"ר קופיאצקי יצר סביבה מזמינה שבה ילדים יכולים ליהנות מביקוריהם אצל רופא השיניים. עם למעלה מ-30 שנות ניסיון, הוא מחויב להבטיח שכל ילד יקבל את הטיפול הטוב ביותר האפשרי. המומחיות של ד"ר קופיאצקי, בשילוב עם התשוקה שלו לרפואת שיניים לילדים, הופכים אותו לבחירה מצוינת לצרכים הדנטליים של ילדכם.ל

פרסומים
פרקים מאת ד"ר ארי קופיאצקי
ד”ר ארי קופיצקי ידוע בעבודת העריכה שלו בספר הלימוד המכונן:ל
Wright’s Behavior in Dentistry for Children.
הוא גם מחברם של כמה יצירות משמעותיות אחרות.ל
Wright’s Behavior in Dentistry for Children.
הוא גם מחברם של כמה יצירות משמעותיות אחרות.ל

- Kupietzky A (2021) Wright’s Behavior Management in Dentistry for Children, 3rd Edition ,Wiley-Blackwell.
- Wright GZ, Kupietzky A (2014) Behavior Management in Dentistry for Children, 2nd Edition ,Wiley-Blackwell.
- Kupietzky A (2004) DOWN’S SYNDROME: INFORMING THE PARENTS in Jewish Medical Ethics. (Halperin M, Fink D, Glick S Eds.) The Dr. Falk Schlesinger Institute for Medical- Halachic Research, Jerusalem, 277-291
- Fuks A, Kupietzky A, Guelmann M (2012) PULP THERAPY FOR THE PRIMARY DENTITION in Pediatric Dentistry: Infancy Through Adolescence / 5th Edition. Mosby
- Kupietzky A Shapira J. (2014) USE OF HUMOR IN PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY in Behavioral Dentistry, Second Edition. Edited by David I. Mostofsky and Farida Fortune , Wiley-Blackwell ISBN: 9781118272060
- Kupietzky A (2015) PRIMARY INCISOR RESTORATION in Handbook of Clinical Techniques in Pediatric Dentistry. Edited by Jane Soxman. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Kupietzky A (2015) ECTOPIC ERUPTION OF MAXILLARY FIRST PERMANENT MOLAR in Handbook of Clinical Techniques in Pediatric Dentistry. Edited by Jane Soxman. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Fuks A, Kupietzky A, Guelmann M (2019) PULP THERAPY FOR THE PRIMARY DENTITION in Pediatric Dentistry: Infancy Through Adolescence / 6th Edition. Mosby.
- Kupietzky A, Gelbier S. (2022) Foreword to the 11th edition of Mcdonald and Avery’s Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent: a historical review. xi-xii In Mcdonald and Avery’s Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent 11th edition. Edited by Dean JA.
- Kupietzky A (2022) PRIMARY INCISOR RESTORATION in Handbook of Clinical Techniques in Pediatric Dentistry. 2nd ed Edited by Jane Soxman. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Kupietzky A (2022) ECTOPIC ERUPTION OF MAXILLARY FIRST PERMANENT MOLAR in Handbook of Clinical Techniques in Pediatric Dentistry 2nd ed. Edited by Jane Soxman. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Townsend JA, Kupietzky A. (2023) BEHAVIORAL APPROACHES AS AN ADJUNCT FOR PULP THERAPY in Contemporary Endodontics for Children and Adolescents. Edited by Fuks, AB, Moskovitz M, Tickotsky N. Springer.
- Levi – Schaffer F. and Kupietzky A. (1990). Mast Cells Enhance Migration and Proliferation of Fibroblasts Into an in vitro Wound. Experimental Cell Research. 188: 42 – 49.
- Levi – Schaffer F., Klapholtz L., Kupietzky A, Weinrauch L., Okun E. (1991) Increased Mast Cells in Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Histochemical Study. Acta Dermato – Venereologica. 71:269 – 271.
- Kupietzky A. (1991) Downs Syndrome: Telling the Parents – Guidelines with a Jewish Perspective. Journal of Jewish Medical Ethics. 1:11 – 16.
- Kupietzky A (1993) HOME: learning process? Pediatric Dentistry 15: 235
- Kupietzky A, Houpt MI. (1993). Midazolam: A review of its use for conscious sedation of children. Pediatric Dentistry 15: 237 – 241. (The paper was included in the required reading list of the American Board of Pediatric Dentistry 1994-2003)
- Kupietzky A and Rozenfarb N (1993). Enamel pearls in the primary dentition: report of two cases. Journal of Dentistry for Children. 60:63 – 66
- Kupietzky A. (1993). Teaching kindergarten and elementary school children dental health: A practical Presentation. The Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 17: 255 – 259
- Kupietzky A, Houpt MI, Melberg J, Shey Z. (1994). Fluoride exchange from glass ionomer preventive resin restorations. Pediatric Dentistry. 16:340 – 345.
- Kupietzky A and Houpt M.I (1995). Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: Characteristics and treatment. Quintessence International 26: 285 – 291.
- Kupietzky A, Holan, G, Shapiro J. (1996). Intranasal midazolam better at effecting amnesia after sedation than oral hydroxyzine: a pilot study. Pediatric Dentistry 18: 32 – 4.
- Houpt M, Kupietzky A, Tofsky N, Koenigsberg SR (1996). Effects of nitrous oxide on diazepam sedation of young children. Pediatric Dentistry 18: 236 – 241
- Kupietzky A, Levi – Schaffer F. (1996) The role of mast cell – derived histamine in the closure of an in vitro wound. Inflammation Research 45: 176 – 80.
- Shapira J, Holan G, Botzer A, Kupietzky A, Tal E, Fuks AB (1996). The effectiveness of midazolam and hydroxyzine as sedative agents for young pediatric dental patients. J Dent Child 63:421 – 25.
- Rozenfarb N, Kupietzky A, Shey Z. (1997) Milk and egg albumen are superior to human saliva in preserving human skin fibroblasts. Pediatric Dentistry 19: 347 – 48
- Kupietzky A, (1997) Strive for excellence and you shall succeed. Pediatric Dentistry 19:452
- Kupietzky A, Blumenstyk A. (1998). Comparing the behavior of children treated using general anesthesia with those treated using conscious sedation. J Dent Child 65: 122 – 27.
- Kupietzky A, Guedalia JS, Tanenbaum A. (1998) Canavan disease – an expanded role for dentists. Spec Care Dentist 18: 119 – 22.
- Kupietzky A (1999) Managing the extremely difficult child: Is general anesthesia the correct solution? Pediatric Dentistry 21: 5
- Kupietzky A. (1999) Treatment of an undiagnosed pre – eruptive intra – coronal radiolucency. Pediatric Dentistry 21: 369 – 72.
- Tal E, Kupietzky A. (2000) Orthodontic alignment of permanent incisors following previous trauma of a primary tooth. Pediatric Dentistry 22: 71 – 2.
- Kupietzky A. (2000) Detection of dens invaginatus in a one – year old infant. Pediatric Dentistry 22: 148 – 50.
- Kupietzky A. (2000) Clinical guidelines for treatment of impalement injuries of the oropharynx in children. Pediatric Dentistry 22: 229 – 31
- Kupietzky A. (2000) Correction of ectopic eruptions of permanent molars utilizing the brass wire technique. Pediatric Dentistry 22:408 – 12.
- Kupietzky A, Rotstine I, Kischinovsky D. (2000) A multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of an intruded maxillary permanent incisor complicated by the presence of two mesiodentes. Pediatric Dentistry 22:499 – 503.
- Waggoner W F, Kupietzky A. (2001). Anterior esthetic fixed appliances for the preschooler: considerations and a technique for placement. Pediatric Dentistry 23: 147 – 50.
- Kupietzky A. (2001) The treatment and long-term management of severe multiple avulsions of primary teeth in a 19-month-old child. Pediatric Dentistry 23: 517 – 21.
- Kupietzky A (2002) Bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors. Pediatric dentistry 24: 145 – 48.
- Kupietzky A, Holan G (2003) Treatment options for crown fractures with pulp exposure in primary incisors. Pediatric Dentistry 25: 241-47.
- Kupietzky A, Flatiz CM, Zeltser R (2003) Eruption of a severely displaced second permanent molar following surgical removal of an odontoma. Pediatric Dentistry 25:378-82.
- Kupietzky A, Waggoner WF, Galea J (2003): The clinical and radiographic success of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors. Pediatric Dentistry 25: 577-81.
- Kupietzky A (2004) Dental teachers or dental technicians? Pediatric Dentistry 15: 235.
- Kupietzky A, Waggoner WF (2004): Parental satisfaction with bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors. Pediatric Dentistry 26: 337-340.
- Shapira J, Kupietzky A, Fuks AB, Holan G (2004): Comparison of oral midazolam with and without hydroxyzine in the sedation of young children. Pediatric Dentistry 26:492-496.
- Zilberman U, Smith P, Kupietzky A, Mass E (2004): The Effect of Hereditary Disorders on Tooth Components: A Radiographic Morphometric Study of Two Syndromes. Archives of Oral Biology. 49:621-629.
- Mass E, Kupietzky A, Maye F, Bimstein E (2004): Alveolar bone height in infraoccluded primary teeth. The Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 28: 221-224.
- Kupietzky A (2004) Strap him down or knock him out: is restraint with conscious sedation an alternative to general anesthesia? British Dental Journal 196: 133–138.
- Kupietzky A, Waggoner WE, Galea J (2005).Long-term photographic and radiographic assessment of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors: results after 3 years. Pediatric Dentistry. 27:221-5.
- Kupietzky A, Majumdar AK, Shey Z, Binder R, Matheson PB (2005). Colony forming unit levels of salivary Lactobacilli and Streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients. J Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.30:51-3.
- Kupietzky A, Botzer E (2005) Ankyloglossia in the infant and young child: clinical suggestions for diagnosis and management. Pediatr Dent. 27:40-6.
- Kupietzky A, Ram D (2005). Effects of a positive verbal presentation on parental acceptance of passive medical stabilization for the dental treatment of young children. Pediatric Dentistry 27:380-384.
- Shafran Y, Kupietzky A (2005) General anesthesia or conscious sedation with restraint: Treating the young child from a Jewish ethical perspective. Journal of Jewish Medical Ethics. 5: 29-39.
- Ziskind D, Kupietzky A, Beyth N (2005): First choice treatment alternatives for caries removal using the chemo-mechanical method. Quintessence Int 36:9-14
- Spira G, Kupietzky A (2005): Oral Defensiveness: Children with a dysfunction of sensory regulation. The Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 29:119-22.
- Kupietzky A (2005). Treating very young patients with conscious sedation and medical immobilization: a Jewish perspective. Alpha Omegan. 98:33-7.
- Kupietzky A (2006) Effects of video information on parental preoperative anxiety level and their perception of conscious sedation vs. general anesthesia for the dental treatment of their young child. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2006 Winter;31(2):90-2.
- Kupietzky A (2007): Clinical Technique: Removable appliance therapy for space maintenance following early loss of primary molars. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry 8 (Suppl. 1) 30-34.
- Vargas KG, Nathan JE, Qian F, Kupietzky A (2007). Use of restraint and management style as parameters for defining sedation success: a survey of pediatric dentists. Pediatr Dent. 2007 May-Jun;29(3):220-7.
- Kupietzky A, Tal E. (2007) The transpalatal arch: an alternative to the Nance appliance for space maintenance. Pediatr Dent. 2007 May-Jun;29(3):235-8.
- Fuks AB, Kupietzky A (2007). Assessment of two curing systems in a self-etching primer/adhesive sealant: a preliminary study for a clinical trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2007 Sep;8(3):171-4.
- Kupietzky A. (2007) The art and science of pediatric dentistry. Pediatr Dent. 2007 Jan-Feb;29(1):6-7.
- Fuks A, Kupietzky A (2007). Assessment of two curing systems in a self-etching primer/adhesive sealant: A preliminary study for a clinical trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 8:171-4.
- Kupietzky A. (2008). Early Childhood Caries: Pretreatment parental counseling and patient preparation. Journal of practical hygiene:17: 6-11.
- Kupietzky A. Tal E, Shapira Y, Ram D. (2008) Fasting state and episodes of vomiting in children receiving nitrous oxide for dental treatment. Pediatr Dent 30:414-9
- Psaltis G. Kupietzky A (2008). A simplified isolation technique for placement of composite strip crowns. Pediatr Dent 30:436-8
- Kupietzky A, Vargas KG, Waggoner WF, Fuks AB (2010).Use of coolant for high-speed tooth preparation: a survey of pediatric dentistry residency program directors in the United States. Pediatr Dent. 32:212-7.
- Fuks A, Guelmann M, Kupietzky A (2012). Current developments in pulp therapy for primary teeth: an update review. Endodontic Topics 23: 50-72.
- Kupietzky A, Tal E, Vargas KG (2012). Development of a parental cooperation scale for use in the pediatric dentistry setting: reliability and criteria. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 37(2):157-61.
- Kupietzky A, Vargas KG, Waggoner WF, Fuks AB (2013).Use of coolant for high-speed tooth preparation: a survey of pediatric dentist members of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Pediatr Dent. Jan-Feb; 35(1):18-22.
- Kupietzky A, van Duinen R. (2015) Report on the clinical technique of thermo-curing glass-ionomer sealant. Quintessence Int. 46 (8):699-705.
- Tal E, Kupietzky A, Fuks A Moskovitz M (2017) Clinical performance of heat-cured high-viscosity glass ionomer class II restorations in primary molars: a preliminary study. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry1. 41(4):264-270.
- Kupietzky A, Fuks A. (2018) The Keeper of the Meaning and the Era of Evidence Based Dentistry. Pediatr Dent. 2018; 40 (4):250-2.
- Kupietzky A Joachim D, Tal E, Moskovitz M (2019) Long-term clinical performance of heat-cured high-viscosity glass ionomer class II restorations versus resin-based composites in primary molars: a randomized comparison trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.
- Gelbier S, Kupietzky A, Tsai TA (2019). History of the International Association of Paediatric Dentistry: A 50-year perspective. Int J Paediatr Dent.
- Kupietzky A . (2019) Global Cooperation: Defining Early Childhood Caries. J Dent Child (Chic). 2019 May 15;86(2):71-72
- Yanover L, Tickotsky N, Waggoner W, Kupietzky A, Moskovitz M. (2020). Zirconia crown performance in primary maxillary anterior teeth: a retrospective photographic and radiographic cohort study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.
- Gelbier S, Kupietzky A. Books on Children's Dental Health and Their Authors. J Hist Dent. 2020 Winter;68(3):145-156. PMID: 33789784.
- Yanover L, Waggoner W, Kupietzky A, Moskovitz, M, Tickotsky N. (2021) Parental and dentist satisfaction with primary anterior zirconia crowns: a retrospective cohort study. Children 2021, 8, 451.
- Tsai AT, Chan HC, Chang YH, Kupietzky A. Staining Outcomes of Silver Diamine Fluoride as an Adjunct in Caries Risk Assessment: A Case Series Evaluation. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Jan 1;46(1):6-11.
- Agouropoulos A, Seymen F, Kupietzky A, Bönecker M. Global overview on current paediatric dentistry teaching: A survey of National Member Societies of the IAPD. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2024 Jan;34(1):58-65.
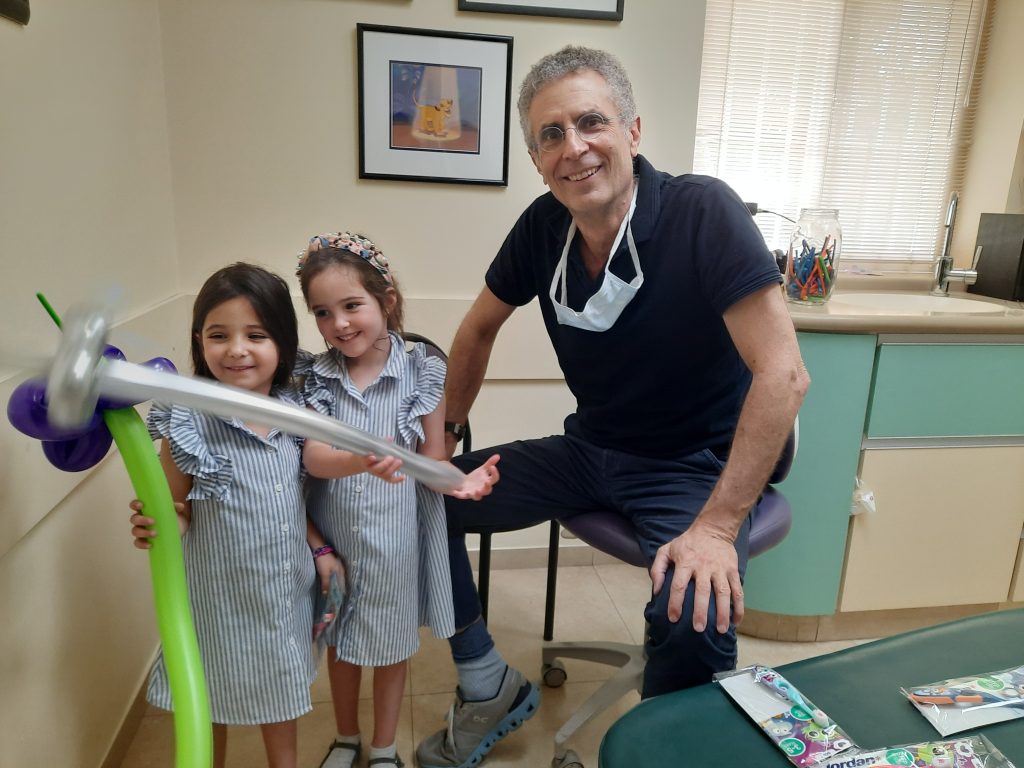
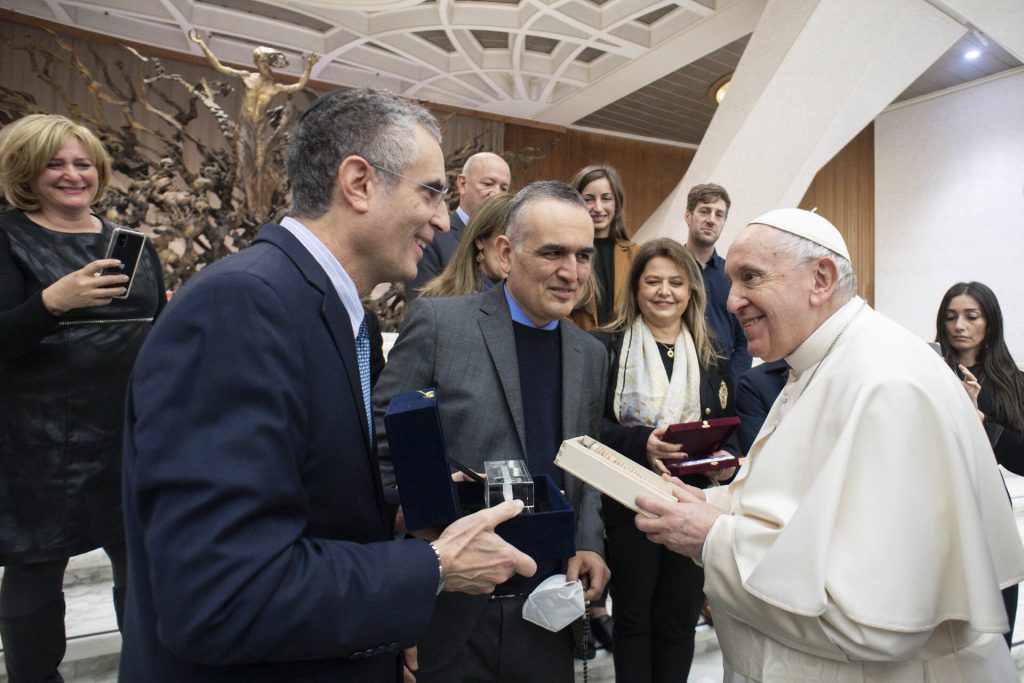
פגישה עם שני רופאי השיניים לילדים הגבוהים ביותר בעולם!ל
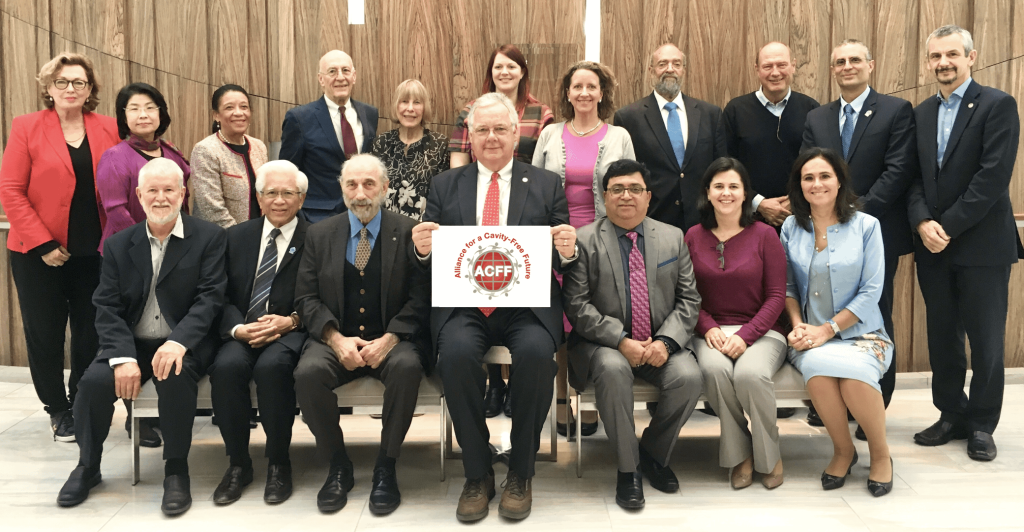
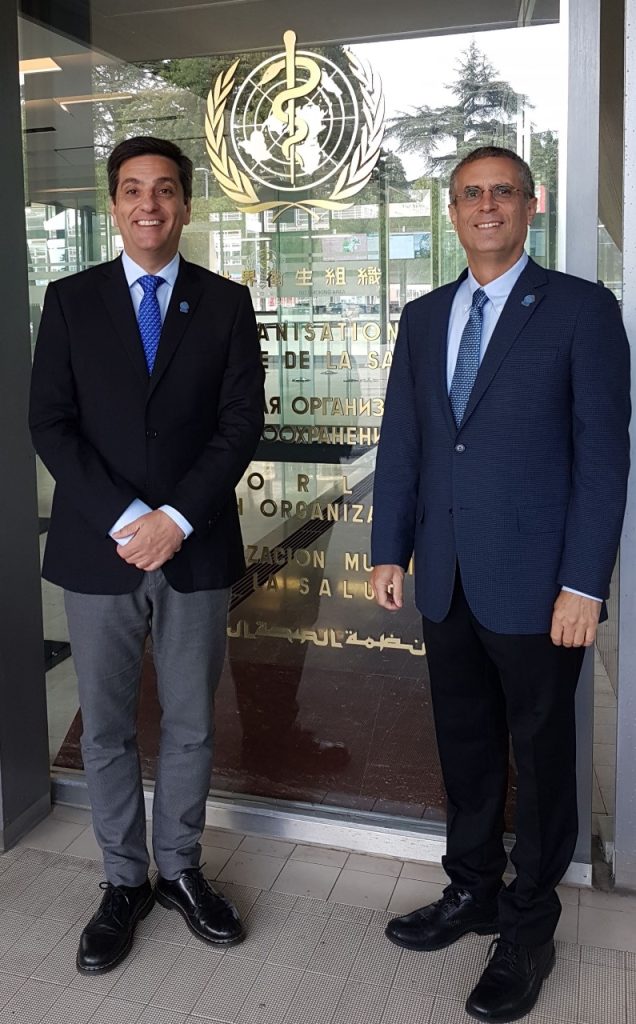
הרצאות ברפואת שיניים לילדים
ד”ר ארי קופיאצקי הוא רופא שיניים לילדים מוסמך על ידי המועצה האמריקאית. ד”ר ארי הוא רופא בכיר במחלקת רפואת שיניים לילדים בבית הספר לרפואת שיניים של הדסה בירושלים ומרצה בנושא רפואת שיניים לילדים ברחבי העולם.ל
מלמד רפואת שיניים באפריקה
מגזין "משפחה" משוחח עם ד"ר ארי

עדויות מלקוחותינו
ד"ר ארי קופיאצקי

אם אתם הורים המחפשים רופא שיניים לילדים מוסמך, מקצועי ואחראי שיכול להתחבר בצורה קסומה לילדיכם כדי שחווייתם אצל רופא השיניים לא תהיה מפחידה ומאיימת אלא מהנה ומשעשעת - אל תחפשו עוד! ד"ר ארי הוא רופא השיניים למשפחתכם! ככל שהילדים והשיניים שלהם גדלים - אתם בידיים טובות ובטוחות עם ד"ר ארי. כל מה שאתם יכולים לחפש ברופא שיניים לילדים - זה ד"ר ארי!ל
רחוב מסילת ישרים 13
ירושלים
קומת קרקע
נגישות לכיסאות גלגלים
סיור במרפאה
הכירו את ד"ר ארי
© 2024 ד"ר ארי קופיאצקי. כל הזכויות שמורות






























